Mastering the Art of Salad Creation


Intro
Salad-making is an art that transcends mere culinary skills. It involves understanding the components that create harmony on a plate while delivering nutrition and visual appeal. The beauty of a salad lies in its versatility; you can play with various ingredients, textures, and flavors to match your preferences. Whether you are a novice cook or a seasoned chef, this guide to crafting a perfect salad will arm you with knowledge and practical tips.
Many people steer clear of salads, thinking they are dull or unfulfilling. This misconception is worth challenging. With the right approach, salads can become the centerpiece of your meals, not just a side dish. This guide aims to demystify the process, making salad preparation approachable and efficient for everyone.
In the following sections, you will discover:
- Essential components that make a salad appetizing.
- Different types of salads suited for various occasions.
- Practical tips for efficient preparation, to make the process smoother, especially for busy individuals.
- Nutritional insights to highlight the health benefits of focused salad compositions.
- Creative variations to accommodate dietary requirements or personal tastes.
Prepare to dive into the deeper aspects of salad-making, revealing how simple ingredients can yield extraordinary results.
Understanding Salads
Salads serve as an important part of modern culinary experiences. Understanding salads is crucial, as it lays the foundation for creating a variety of dishes that are both delicious and health-conscious. Salads are versatile and can be adapted to meet different dietary needs, preferences, and cultural influences. Therefore, grasping the essence of salads allows cooks to craft meals that cater to specific palates while ensuring nutritional value.
Definition and Purpose
A salad is typically a dish consisting of mixed ingredients, primarily vegetables, fruits, or grains, accompanied by dressings. While the term "salad" can refer to a range of dishes, it primarily denotes a cold dish intended to be served either as an appetizer or a side. The purpose of salads extends beyond mere sustenance; they are a canvas for culinary creativity and can be nutritionally dense when prepared thoughtfully. Salads are often characterized by their refreshing nature and the balance they provide in a meal. The act of combining different textures and flavors through various components allows an exploration of taste and health benefits.
Nutritional Benefits
Salads are often seen as a cornerstone of balanced diets due to their high nutrient density. They typically contain an array of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, significant for maintaining good health. Leafy greens, for example, can be rich in Vitamin K and folate, while adding colorful vegetables enhances a salad's nutrient profile. Furthermore, including proteins and healthy fats can convert a simple salad into a complete meal that contributes to overall well-being.
For health-focused individuals, incorporating a variety of ingredients in salads is not only satisfying but can also lead to increased feelings of fullness, potentially aiding in weight management.
Salads provide a wealth of nutrients that contribute to a healthier lifestyle, making them a wise choice for conscious eaters.
In addition to benefiting physical health, salads offer a way to incorporate seasonal and local produce, promoting sustainable eating habits. This connection to nature and food can enhance one's appreciation for culinary traditions and foster deeper relationships with food.
Fundamental Components of a Salad
The fundamental components of a salad are critical to creating a dish that is not only enjoyable to eat but also visually appealing and nutritionally balanced. Understanding each component helps in selecting the right ingredients, ensuring salads meet both taste and health requirements. A well-crafted salad can serve as a satisfying meal or a delightful side, making it an essential dish in modern culinary practices.
Base Ingredients
Base ingredients form the foundation of any salad. These components bring volume, texture, and essential nutrients to the dish.
Leafy Greens
Leafy greens are often the primary base for most salads. Popular choices include romaine, spinach, and arugula. The key characteristic of leafy greens is their high vitamin content. They are a good source of vitamins A, C, and K, which are important for overall health. Moreover, they are low in calories, making them an excellent choice for those watching their weight.
A unique feature of leafy greens is their ability to absorb dressings and flavors well, enhancing the overall taste of the salad. However, a disadvantage could be their short freshness lifespan; without proper storage, they can wilt quickly.
Vegetables
Vegetables add crunch and flavor to salads. Common vegetables include cucumbers, bell peppers, and carrots. The key characteristic of vegetables is their rich fiber content, which aids digestion. Including a variety of colors can promote a diverse nutrient profile, making them an essential addition to any salad.
One unique feature of vegetables is their versatility in texture and taste; raw vegetables provide crunch, while roasted ones offer depth of flavor. However, selecting the right vegetable is important as some are more suitable for certain types of salads than others.
Fruits
Fruits provide a sweet contrast to salty and savory salad components. Apples, berries, and citrus fruits are popular choices. The key characteristic of fruits is their high natural sugar content and vitamins, particularly vitamin C. Fruits can elevate the salad’s flavor profile, adding brightness.
A unique aspect of fruits is their ability to complement both leafy greens and proteins, making them a versatile option. An advantage is that they can also contribute healthy carbohydrates to the meal. However, one should be cautious about the balance of sweetness, as too much fruit can overpower the other ingredients.
Proteins
Proteins are an essential component of salads, providing substantial nutritional value and improving satiety. They can be derived from various sources to cater to different dietary preferences.
Meat Options
Meat options like chicken, turkey, or shrimp add substance to salads. The key characteristic of meat is its high protein content, which is important for muscle repair and growth. It can make a salad more filling, transforming it into a complete meal.
A unique feature of meat is the variety it introduces in flavors and textures. Grilled or roasted meat can enhance the taste profile of a salad. However, overcooking or misseasoning meat can lead to a dry or bland experience.
Plant-Based Proteins
Plant-based proteins include beans, lentils, or tofu. They are becoming increasingly popular due to their health benefits and suitability for vegetarian diets. The key characteristic is their fiber and nutrient-rich profile. They offer a hearty alternative to meat and cater to various dietary preferences.
One unique feature of plant-based proteins is their versatility in salads. They can be cooked or served raw, depending on preference. An advantage is they often come with lower fat content compared to animal proteins. Yet, they can require proper seasoning to enhance their flavor.
Cheeses

Cheeses, such as feta, mozzarella, or parmesan, can add richness to salads. The key characteristic of cheeses is their creaminess, which can balance the textures of other ingredients. They offer protein and calcium, making them a beneficial choice.
Cheese's unique feature is its ability to pair well with both vegetables and fruits, adding depth to the dish. However, excessive cheese can lead to higher calorie counts.
Fats and Dressings
Fats and dressings are crucial for flavor and texture. They tie together the flavors of the salad and enhance the absorptive qualities of other ingredients.
Types of Oils
Types of oils such as olive oil, avocado oil, or sesame oil can significantly impact the flavor of a salad. The key characteristic of oils is their healthy fat content, particularly unsaturated fats that support heart health. They help in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins from the salad components.
A unique feature of oils is their potential for flavor enhancement. Different oils bring unique tastes and aromas to salads. However, one must be cautious as too much oil can lead to excessive calories.
Vinegars
Vinegars like balsamic, apple cider, or red wine vinegar add acidity to salads. The key characteristic of vinegars is their ability to brighten flavors while providing a tangy twist. They balance the richness of oils, making for a harmonious dressing.
A unique feature of vinegars is the variety in flavors they offer. For example, balsamic vinegar can add sweetness, while apple cider vinegar gives a more pungent flavor. A disadvantage may include their strong flavor being overwhelming to some salads if used excessively.
Creative Dressings
Creative dressings encompass diverse combinations, such as yogurt-based or tahini dressings. The key characteristic is their personalization; they can fit a standard salad to individual tastes. Creative dressings can combine healthy fats and flavors, enhancing nutritional value without compromising taste.
A unique feature of creative dressings is their ability to incorporate unique ingredients like herbs and spices. This adds depth and prevents monotony in salads. However, crafting a balanced dressing requires knowledge of flavor profiles.
The right combination of base ingredients, proteins, and fats/dressings ensures your salad is not only visually appealing but also nutritious. A well-prepared salad supports a healthy lifestyle.
Types of Salads
Understanding the various types of salads is essential for anyone looking to craft a perfect salad. Each category offers unique flavors, textures, and nutritional benefits, making salads an incredibly versatile dish. From light and refreshing to hearty and filling, knowing the distinctions can significantly enhance your meal prep. This section will cover several common types of salads and highlight their key characteristics.
Green Salads
Green salads are perhaps the most familiar and widely consumed. They primarily consist of leafy greens such as romaine, spinach, or arugula. The appeal of green salads lies in their fresh taste and nutritional value. Leafy greens are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
They can be customized easily by adding other ingredients like vegetables, nuts, seeds, or fruits. Common additions may include tomatoes, cucumbers, or bell peppers. For a more substantial dish, proteins like chicken or chickpeas can also be included.
Pasta Salads
Pasta salads bring a distinct richness and heartiness to the table. They generally feature cooked pasta mixed with various ingredients like vegetables, cheese, and even meats. The type of pasta used can greatly affect the final texture and taste. Varieties like fusilli or penne are popular due to their ability to hold dressing well.
Benefits of Pasta Salads:
- Filling option for lunch or dinner
- Can serve as a side dish or main course
- Versatile with dressing selections
Most pasta salads are cold, making them an excellent choice for picnics or barbecues.
Grain-Based Salads
Grain-based salads are another excellent type that provides substance. Common grains include quinoa, farro, or brown rice. These salads are often rich in fiber and proteins, offering a hearty yet healthy option.
They can be crafted with an assortment of vegetables and dressings. The grains serve as a base that absorbs flavors effectively, creating a cohesive dish. Adding nuts or dried fruits can enhance the texture and flavor complexity.
Fruit Salads
Fruit salads are unique in their refreshing taste and natural sweetness. They primarily consist of fresh fruits, making them an appealing choice for summer gatherings. The vibrant colors and flavors are visually enticing and can be a delightful option for desserts or snacks.
Combining various fruits like berries, melons, and citrus provides a range of nutrients. You can also consider enhancing a fruit salad with mint or a squeeze of lime for additional freshness.
Protein Salads
Protein salads focus on incorporating a significant protein element, such as beans, tofu, or meats. Their dense nutritional value makes them excellent for fueling the body and keeping energy levels steady.
These salads can be particularly beneficial for those who follow specific dietary restrictions or are looking to increase protein intake. Popular options include tuna salad or chicken Caesar salad, which are both filling and nutritious.
Overall, understanding these types of salads allows for more creativity in the kitchen. Not only do they cater to diverse palates, but they also help meet varying nutritional needs.
"Salads can be a canvas for your culinary creativity, and knowing the different types provides a strong foundation."
Preparing Your Salad
Preparing your salad involves several crucial steps that greatly influence the final outcome. This process is often overlooked, yet it ensures that the salad not only tastes delightful but also retains its nutritional value. Each stage of preparation allows you to customize flavors and textures, enabling a tailored experience for anyone enjoying the salad. By honing in on selecting fresh ingredients, properly washing and drying, and mastering chopping techniques, you can elevate your salad-making skills significantly.
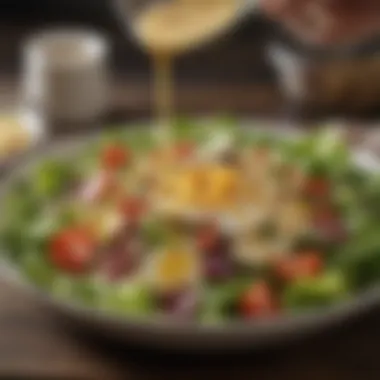

Selecting Fresh Ingredients
Fresh ingredients serve as the foundation for any good salad. The choice of products directly impacts flavor, texture, and even nutritional benefits. There are some key points to keep in mind when selecting these ingredients:
- Seasonality: Opt for produce that is in season. This often ensures better flavor and texture, as well as supporting local agriculture.
- Visual Inspection: Look for vibrant colors and firm textures. Wilted leaves or bruised fruits may indicate age or lack of freshness.
- Source: Whenever possible, choose organic options to minimize pesticide exposure and enhance flavor. Local farmers' markets can be a good resource for fresh organic produce.
Moreover, diversity in the ingredients can enhance both the visual appeal and nutritional profile of your salad. Combine leafy greens with a mix of colorful vegetables, fruits, and proteins to create a well-rounded dish.
Washing and Drying Greens
Proper washing and drying of greens is often underestimated but essential for food safety and maximizing flavor. Here are some guidelines to follow:
- Washing: Use cold water to wash leafy greens. Submerge them in water or use a gentle spray from the faucet. This process helps to remove dirt, pesticides, and any lingering insects.
- Drying: Being thorough in drying greens is crucial. Excess moisture can dilute dressings and cause your salad to become soggy. Use a salad spinner for effective drying or place greens in a clean kitchen towel and gently pat them dry.
By handling your greens with care, you not only protect your health but also ensure a more pleasant dining experience.
Chopping Techniques
Chopping is not just about cutting ingredients; it influences the texture and presentation of the salad. Here are some practical techniques:
- Uniform Size: Aim for uniform size in all ingredients to allow for even mixing and an attractive presentation. This means cutting vegetables like cucumbers and carrots into similar dimensions.
- Chopping Styles: Each vegetable may require a different style. For example, leafy greens can be shredded, while harder vegetables can be diced or julienned. Utilize a sharp knife to ensure clean cuts.
- Preservation of Flavors: A rough chop on herbs can help release their essential oils, enhancing the salad's flavor.
Ultimately, these chopping methods contribute significantly to the overall integrity of the salad.
Fresh ingredients, careful washing, and precise chopping are integral to a successful salad-making process.
By paying attention to each of these areas, salad preparation can be both an efficient and rewarding endeavor.
Mixing and Assembling
Mixing and assembling is a pivotal step in the creation of a salad. This stage goes beyond simply combining ingredients; it is essential for maximizing flavor, texture, and presentation. Proper mixing enhances the overall taste and ensures that each bite delivers a balanced experience. When ingredients are not well-mixed, certain flavors may dominate, overshadowing the subtle notes of other components.
Another important consideration is the visual aspect. A well-assembled salad is visually appealing and can stimulate the appetite. The eye is often the first sense to engage with food, and presenting the salad in an attractive manner can make it more enticing. This section discusses two significant components of this stage—layering for visual appeal and effective dressing application.
Layering for Visual Appeal
When constructing a salad, layering plays a crucial role. The method of arranging ingredients can transform a simple dish into a work of art. Begin with the base layer, typically leafy greens, which provide a vibrant foundation. Next, alternate layers of vegetables, proteins, and other toppings. This technique not only enhances aesthetics but also promotes even distribution of flavors.
Consider these tips for effective layering:
- Start With Greens: Place leafy greens as the base. This provides a stable foundation and helps other ingredients stand out.
- Add Height: Incorporate tall ingredients, such as sliced bell peppers or croutons, to create a visual height. This adds interest to the presentation.
- Employ Color Contrast: Use a variety of colored ingredients. For example, mix bright tomatoes with dark greens for an eye-catching contrast.
By layering thoughtfully, the salad can not only taste great but also look appetizing. Each layer should invite curiosity and provoke the desire to dig in.
Dressing Application
The application of dressing is a fundamental aspect of mixing and assembling. It is vital to distribute the dressing evenly to ensure that every component is coated without being oversaturated. There are various methods for applying dressing:
- Drizzle: Lightly drizzling dressing over your salad helps to evenly coat the ingredients. This method avoids clumping and ensures that flavors are well-balanced.
- Tossing: After applying dressing, toss the salad gently. This method incorporates the dressing into the salad, ensuring that each bite offers a uniform flavor.
It is also important to consider dressing type. Dressings made from natural ingredients tend to enhance the salad's flavors. You can use oil and vinegar, yogurt-based dressings, or even homemade mixtures. Remember the goal is to complement the fresh ingredients without overpowering them.
Key Insight: The right amount and application of dressing can elevate the entire salad experience. Too little may render it bland, while too much can make it soggy. Achieving the perfect balance is critical.
Incorporating these techniques into the mixing and assembling phase transforms salads into delightful culinary experiences. The combination of visual appeal and skillful dressing application is what differentiates a simple dish from a remarkable one.
Storing and Serving Salads
Storing and serving salads effectively is crucial for maintaining their freshness, flavor, and nutritional value. Understanding how to properly store salads can extend their shelf life, ensuring they remain appealing and safe for consumption. This section delves into best practices for storage, as well as suggestions for serving that enhance the overall dining experience.
Storage Techniques
Short-term Storage
Short-term storage refers to keeping salads fresh for a day or so after preparation. This method is useful for meal prep and allows busy individuals to have quick meal options available. The primary characteristic of short-term storage is its focus on retaining freshness without compromising taste. By utilizing airtight containers, salads can maintain their crispness for several hours.
One unique feature of short-term storage is the separation of components. Keeping dressings separate from fresh ingredients until serving is beneficial as it prevents sogginess. This practice not only preserves texture but also enhances flavor upon mixing.
The advantages of short-term storage are clear: convenience and immediate accessibility. However, a disadvantage is that it might limit the longevity of more delicate components, like leafy greens.
Long-term Storage
Long-term storage, on the other hand, is about preserving salads for several days or even weeks. This method involves proper wrapping or use of vacuum sealing techniques to minimize spoilage. A key characteristic of long-term storage is the attention to temperature control. Refrigeration is typically essential to keep ingredients safe and fresh over extended periods.


A unique aspect of long-term storage is blanched vegetables. This technique involves briefly boiling vegetables and then cooling them rapidly, making them more resilient when stored. The advantage of long-term storage is clear: it allows individuals to prep meals in advance, reduce food waste, and enjoy salads at later dates. Still, it can lead to a loss of texture in fresh ingredients, especially greens, which may not hold up as well compared to short-term storage methods.
Serving Suggestions
When it comes to serving salads, presentation is key. Visually appealing arrangements can elevate the dining experience. Here are some suggestions:
- Layering: Build salads in layers. Start with heavier ingredients at the bottom and lighter ones on top for stability.
- Garnishes: Use fresh herbs or edible flowers for a pop of color.
- Platter Ideas: For gatherings, consider using a large platter for a shared salad. It encourages communal dining.
- Dressing on the Side: Offering dressing separately allows guests to customize their servings according to their taste preferences.
Remember: The goal is to make salads not just a meal but an experience.
In summary, mastering the art of storing and serving salads ensures that they remain fresh and enjoyable. Efficiency plays a significant role, particularly for those with hectic lifestyles. From proper storage methods to appealing serving techniques, these practices are pivotal in creating salads that impress.
Special Dietary Considerations
In the culinary world, understanding special dietary considerations is important, especially when it comes to salad preparation. Salads are often seen as a healthy option, but they can cater to specific dietary needs as well. Individuals today are more health-conscious and look for meals that align with their preferences, whether for medical reasons or personal lifestyle choices. Addressing gluten-free, vegan, vegetarian, and low-calorie diets in salad making not only broadens appeal but also enhances accessibility and inclusivity in dining.
Gluten-Free Options
For those who are sensitive to gluten or have celiac disease, it is essential to focus on gluten-free ingredients. Most fresh vegetables and fruits are naturally gluten-free, making them safe for inclusion in salads. When selecting dressings, it is crucial to check labels for potential gluten contaminants. Options such as olive oil, vinegar, and fresh herbs are excellent choices that can add flavor without gluten. It’s also beneficial to consider grains that are gluten-free, like quinoa and rice, which can provide more substance to the salad. Here are some ideas:
- Use corn tortillas for croutons instead of traditional breads.
- Incorporate gluten-free grains as bases or fillers.
- Experiment with gluten-free dressings available in the market.
Vegan and Vegetarian Variations
Vegan and vegetarian salads have gained popularity due to the increased awareness and demand for plant-based diets. Preparing salads that align with these diets not only satisfies the taste buds but also enhances nutrition. Vegan salads exclude all animal products, while vegetarian options may include dairy or eggs. Key components include:
- Leafy Greens: Such as spinach, kale, or romaine, are fundamental.
- Plant Protein Sources: Foods like chickpeas, black beans, and tofu are great for protein.
- Nuts and Seeds: Including chia seeds, walnuts, or almonds adds crunch and nutritional value.
Consider making use of ingredients like nutritional yeast for cheesy flavor in a vegan context. This creates a more profound experience in terms of both texture and taste.
Low-Calorie and Low-Fat Salads
Low-calorie and low-fat salads can help maintain a healthy lifestyle without sacrificing flavor. These salads are often characterized by an abundance of fresh vegetables and minimal use of high-calorie dressings. Focusing on high water content vegetables can make a salad more filling while keeping calories in check. Some effective strategies include:
- Opting for vinegar-based dressings instead of creamy ones reduces calorie intake.
- Incorporating lean proteins like grilled chicken or shrimp helps in keeping salads satisfying without excess fat.
- Adding bulk with vegetables like cucumbers, carrots, and bell peppers aids in creating volume.
Ultimately, emphasizing special dietary considerations can attract a variety of guests to explore diverse and inclusive salad options. With growing health awareness, offering such options can lead to broader acceptance of salads as a significant part of diet.
Creative Salad Combinations
Creative salad combinations are crucial for elevating the humble salad into a dish that excites both the palate and the eye. By exploring various elements from different cuisines, your salads can become a canvas for flavor and texture exploration. Embracing diversity in ingredients not only enhances taste but also encourages a more healthful diet. This section dives into global influences and seasonal ingredients, shedding light on how they contribute to innovative salad creations.
Global Influences
In today's culinary landscape, global influences play a significant role in crafting unique salad combinations. Various cultures bring their own flair to salads, often using local ingredients and traditional flavors. Here are a few examples:
- Mediterranean Salads: These typically feature ingredients like olives, feta cheese, and tomatoes tossed with olive oil. The use of herbs like oregano or basil adds an aromatic profile that is both refreshing and satisfying.
- Mexican Salads: Incorporating black beans, corn, and avocado creates rich textures. A squeeze of lime juice can enhance the flavors, making the salad vibrant and full of life.
- Asian Salads: Ingredients such as sesame oil, soy sauce, and fresh ginger can be used to dress salads, often including crunchy vegetables like bell peppers and carrots. This results in a crunchy, flavorful dish that can be both light and filling.
By integrating these global elements, you not only broaden your culinary repertoire but also promote a healthier variety of nutrients. Engaging in cross-cultural cooking can translate into deeper appreciation for various food traditions and their unique qualities.
Seasonal Ingredients
Utilizing seasonal ingredients is another pivotal aspect of creative salad crafting. Seasonal foods are generally fresher, more flavorful, and often more affordable. By focusing on these, you can ensure that your salads not only taste great but also reflect the time of year.
- Spring: Fresh peas, asparagus, and radishes bring a crisp touch. Combine these with some fresh herbs for an uplifting flavor.
- Summer: Tomatoes, cucumbers, and sweet bell peppers shine during this season. A simple dressing of vinegar can enhance their natural sweetness.
- Fall: Root vegetables like beets and carrots become the star. These can be roasted to amplify their flavor, paired with nuts for added crunch.
- Winter: Leafy greens like kale or winter lettuce provide a hearty base for salads. Pairing them with citrus fruits offers a refreshing contrast.
Using seasonal ingredients not only supports local farmers but also caters to optimal taste and nutrition. Ingredients consumed at their peak maturity are usually at their best in terms of flavor and nutrient density.
"Seasonal eating fosters a stronger connection to food and the environment, leading to a more sustainable lifestyle."
Experimenting with creative combinations enables culinary enthusiasts to break free from the ordinary. It transforms salads from basic sides into main attractions during meals.
Final Considerations
When crafting a perfect salad, final considerations play a vital role. These steps can enhance the final product significantly. Preparing the salad is just the beginning. How you present it, and the final touches you add can elevate the dish.
Presentation Techniques
Presentation is key to making any salad enticing. The visual appeal can sometimes persuade an individual to try something new or eat more of a healthy option. Here are a few techniques that can improve your salad presentation:
- Use a variety of colors. Mixing different colored vegetables and fruits can create a vibrant dish. Green leafy bases combined with bright red tomatoes and yellow peppers not only look appealing but also suggest a range of nutrients.
- Choose the right bowl. The serving dish can affect how your salad is perceived. A clear glass bowl allows the colors of your ingredients to shine. A rustic wooden bowl can give a more natural feel. Select the one that compliments the theme of your meal.
- Layer your ingredients. Instead of mixing everything together, try layering. This creates an organized look and enhances the overall appeal. Start with the leafy base, followed by proteins, colorful vegetables, and finish with nuts or seeds on top.
- Garnish wisely. Fresh herbs or edible flowers can add a touch of elegance to your salad. A sprig of parsley or a few microgreens can provide a refined finish.
A well-presented salad can turn a simple dish into a culinary masterpiece that captures attention and encourages enjoyment.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even experienced cooks can make mistakes when preparing salads. Awareness of common pitfalls helps ensure a successful dish. Here are some errors to avoid:
- Over-dressing. Applying too much dressing can dilute flavors and make greens soggy. It is best to start with a small amount and add more to taste.
- Using old ingredients. Freshness is crucial. Always check the expiry dates on products, especially with leafy greens or perishable items like cheeses and meats.
- Neglecting texture. A salad should have a mix of textures – crunchy, soft, and creamy. Avoid using only one type as it can be monotonous.
- Ignoring the balance of flavors. A salad should balance different taste profiles. Incorporate a mix of sweet, salty, sour, and bitter elements. This keeps the dish interesting and satisfying.
- Not season during preparation. Adding salt and pepper to individual components can enhance their flavor. Don’t wait until the end; season ingredients as you assemble them.
By keeping these final considerations in mind, one can craft an impressive salad that is not only delightful to taste but also visually engaging.







